The subjunctive mood is used to express the affirmative and negative commands of the
Ud.,
Uds., and
nosotros forms, and only the negative commands of the
tú and
vosotros forms. The affirmative
tú commands are not based on the subjunctive. There is however, a list of verbs that are irregular in the affirmative
tú command form that you must learn.
Regular verbs
The most unusual type of command is the form used when you wish to give an affirmative command to someone you would address as tú. Oddly enough, the form of the verb used for an affirmative tú command looks exactly like the present tense él form of the verb: not the present subjunctive but rather the present indicative, and not the tú form but the él form. For this reason, it is common to use the pronoun tú after the command so you can tell the difference between “he does something,” and “you, do something.” For example:
If you remember how to create the present tense él form of the verb in the indicative mood, you can create the affirmative tú command form. If a verb undergoes a stem change in the present tense, the command form will undergo the same stem change. Notice that the subject pronoun may or may not follow a command form.
- Produce más comida ahora.
- Cuenta tú el dinero antes de salir.
- Count the money before leaving.
- Almuerza durante el descanso.
- Eat lunch during the break.
Irregular affirmative tú commands
There are a few affirmative tú commands that are not like the present tense él form of the verb; these are considered irregular. Learn the irregular affirmative tú commands for the seven basic verbs in Table .
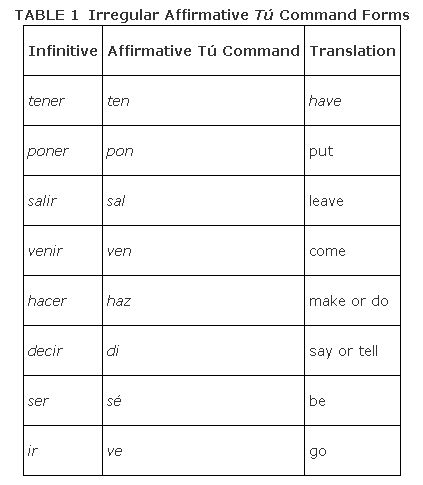
Because the tú command for ser is the same as the present tense yo form of the verb saber, you must consider the context of the sentence in order to determine which of the two is intended. In the following examples, notice how using a subject pronoun clarifies these identical forms with completely different meanings.
- Sé tú médico porque así ganarás mucho dinero.
- Be a doctor because you will earn a lot of money. (affirmative tú command, ser)
- Yo sé que los médicos ganan mucho.
- I know that doctors earn a lot. (present tense yo form, saber)
If you tell someone whom you address as tú not to do something, it is a negative command and, thus, you must use a different form. Only the tú and the vosotros commands have different forms for the negative and the affirmative. For Ud. and Uds. commands, the same form is used for negative and affirmative commands.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|