Forming the Past Subjunctive: Verb Rules
There is another subjunctive tense to use when the subjunctive is necessary but the sentence is in a past tense. Technically, it is called the
imperfect subjunctive, but that title is unnecessarily confusing. There is only one way to put the subjunctive in the past tense, and because it's based on the preterit tense, it's more fitting to call it the “past subjunctive.” Before you can learn how the past subjunctive is used in sentences, however, you must first learn to create the forms.
All verbs, without exception, follow the same rules for forming the past subjunctive; thus, the past subjunctive tense has no irregular verbs. Although that sounds simple, there is one difficulty: The first rule is to start with the third person plural form of the preterit. There are a plethora of verbs that are irregular in the preterit, but once you've remembered the ellos form, you can easily turn the preterit into the past subjunctive.
All verbs end in ‐ron in the third person preterit form. Remove the ‐ron and add the endings in Table .
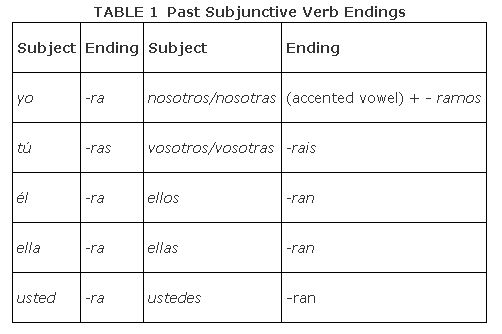
Notice that the vowel in front of the nosotros/nosotras ending must have an accent mark. As you can see in the tener example in Table , that is é for some verbs. And as you can see in Table , á may be the accented vowel in front of some nosotros/nosotras endings.
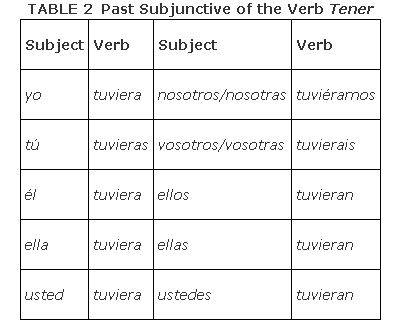
The verb tener in Table serves as a good example because it shows how different a verb can look in the past subjunctive due to the fact that the ellos preterit form often has little in common with the infinitive form.
Remember the following rule:
- Preterit ellos form: tuvieron minus the ‐ron = tuvie‐
Remember the following rule:
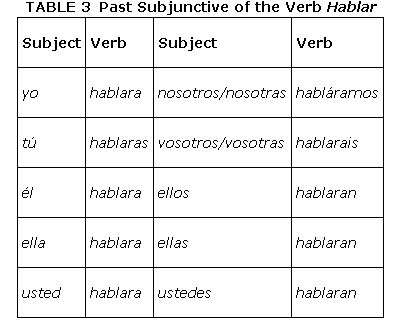
- Preterit ellos form: hablaron minus the ‐ron = habla‐
There is another set of endings, which is less frequently used, that can be used instead of the ‐ra/‐ras/‐ramos/‐rais/‐ran endings to create the past subjunctive. In Table , notice that the letters ‐se replace ‐ra in every form. To use these endings, you must also use the ellos form of the preterit minus the ‐ron ending. There is no special reason why you would have to use the ‐se endings because they are exactly the same as the ‐ra endings; just be prepared to understand what they mean when you hear or see them.
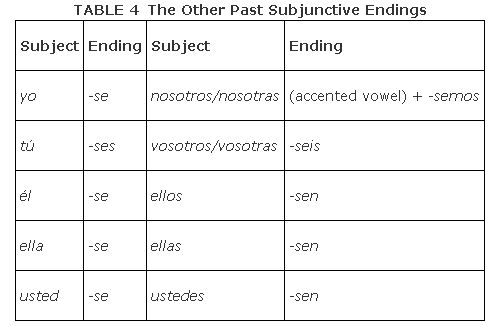
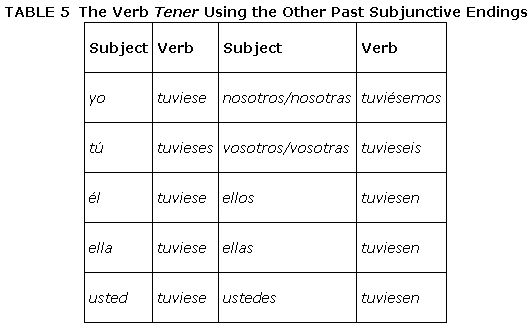
Remember the following rule:
- Preterit ellos form: tuvieron minus the ‐ron = tuvie‐
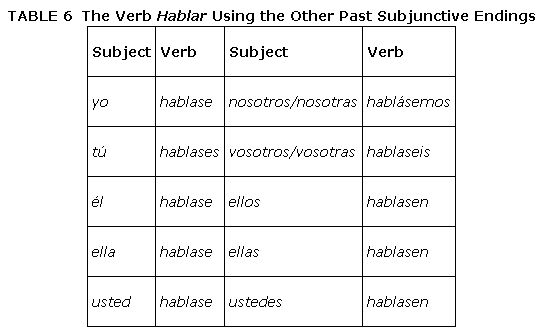
There are so many irregularities in the preterit tense that it is necessary to review the preterit tense with a special focus on the third person plural (ellos) form.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|