- Positioning power. Positioning power measures the amount of power or authority a manager perceives the organization has given him or her for the purpose of directing, rewarding, and punishing subordinates. Positioning powers of managers depends on the taking away (favorable) or increasing (unfavorable) of the decision‐making power of employees.
Fiedler then rated managers as to whether they were relationship oriented or task oriented. Task‐oriented managers tended to do better in situations with good leader/member relationships, structured tasks, and either weak or strong position power. They also did well when the tasks were unstructured but position power was strong, as well as when the leader/member relations were moderate to poor and the tasks were unstructured. Relationship‐oriented managers, on the other hand, do better in all other situations.
The task‐motivated style leader experiences pride and satisfaction in task accomplishment for his or her organization, while the relationship‐motivated style leader seeks to build interpersonal relations and extend extra help for team development in his or her organization.
Judging whether a leadership style is good or bad can be difficult. Each manager has his or her own preferences for leadership. Task‐motivated leaders are at their best when their teams perform successfully—such as achieving new sales records or outperforming major competitors. Relationship‐oriented leaders are at their best when greater customer satisfaction is gained and positive company images are established.
Hersey-Blanchard's situational model
The Hersey‐Blanchard Model of Situational Leadership, shown in Figure , is based on the amount of direction (task behavior) and amount of socioemotional support (relationship behavior) a leader must provide given the situation and the level of maturity of the followers.
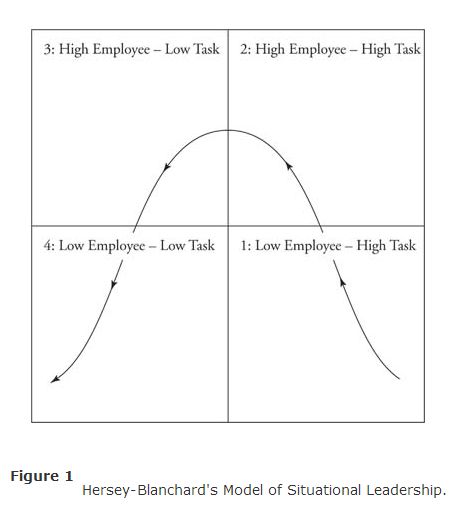
Task behavior is the extent to which the leader engages in spelling out the duties and responsibilities to an individual or group. This behavior includes telling people what to do, how to do it, when to do it, and where to do it. In task behavior, the leader engages in one‐way communication. Relationship behavior, on the other hand, is the extent to which the leader engages in two‐way or multiway communications. This behavior includes listening to, facilitating, and supporting employees. And maturity is the willingness and ability of a person to take responsibility for directing his own behavior. Employees tend to have varying degrees of maturity, depending on the specific tasks, functions, or objectives that they attempt to accomplish.
To determine the appropriate leadership style to use in a given situation, a leader must first determine the maturity levels of his or her followers in relationship to the specific task. As employee maturity levels increase, a leader should begin to reduce task behavior and increase relationship behavior until his or her followers reach moderate maturity levels. As the employees move into above‐average maturity levels, the leader should decrease not only task behavior but also relationship behavior.
Once maturity levels are identified, a manager can determine the appropriate leadership style: telling, selling, participating, or delegating.
- Telling. This style reflects high task/low relationship behavior (S1). The leader provides clear instructions and specific direction. Telling style is best matched with a low follower readiness level.
- Selling. This style reflects high task/high relationship behavior (S2). The leader encourages two‐way communication and helps build confidence and motivation on the part of the employee, although the leader still has responsibility and controls decision making. Selling style is best matched with a moderate follower readiness level.
- Participating. This style reflects high relationship/low task behavior (S3). With this style, the leader and followers share decision making and no longer need or expect the relationship to be directive. Participating style is best matched with a moderate follower readiness level.
- Delegating. This style reflects low relationship/low task behavior (S4). Delegating style is appropriate for leaders whose followers are ready to accomplish a particular task and are both competent and motivated to take full responsibility. This style is best matched with a high follower readiness level.
House's path-goal theory
The path‐goal theory, developed by Robert House, is based on the expectancy theory of motivation. A manager's job is to coach or guide workers to choose the best paths for reaching their goals. Based on the goal‐setting theory, leaders engage in different types of leadership behaviors depending on the nature and demands of a particular situation.
A leader's behavior is acceptable to subordinates when viewed as a source of satisfaction. He or she is motivational when need satisfaction is contingent on performance; this leader facilitates, coaches, and rewards effective performance. Path‐goal theory identifies several leadership styles:
- Achievement‐oriented. The leader sets challenging goals for followers, expects them to perform at their highest levels, and shows confidence in their abilities to meet these expectations. This style is appropriate when followers lack job challenges.
- Directive. The leader lets followers know what is expected of them and tells them how to perform their tasks. This style is appropriate when followers hold ambiguous jobs.
- Participative. The leader consults with followers and asks them for suggestions before making a decision. This style is appropriate when followers are using improper procedures or are making poor decisions.
- Supportive. The leader is friendly and approachable. He or she shows concern for the followers' psychological well‐being. This style is appropriate when followers lack confidence.
Path‐goal theory assumes that leaders are flexible and that they can change their styles as situations require. This theory proposes two contingency variables that moderate the leader behavior‐outcome relationship:
- Environment characteristics are outside the control of followers, task structure, authority system, and work group. Environmental factors determine the type of leader behavior required if follower outcomes are to be maximized.
- Follower characteristics are the focus of control, experience, and perceived ability. Personal characteristics of subordinates determine how the environment and leader behavior are interpreted.
Effective leaders clarify the path to help their followers achieve their goals, and make their journeys easier by reducing roadblocks and pitfalls. Research demonstrates that employee performance and satisfaction are positively influenced when leaders compensate for shortcomings in either their employees or the work settings.