The Nature of Criminal Law
To understand criminal law, it is necessary to distinguish criminal from civil law and to know the difference between substantive and procedural law.
Criminal law versus civil law
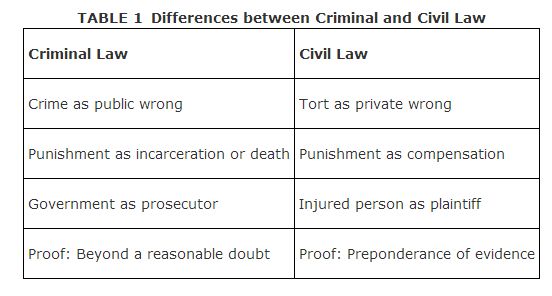
All law other than criminal law is known as civil law. It includes tort law (private wrongs and damages), property law, and contract law. Differences between criminal law and civil law are important because criminal proceedings are separate from civil actions. Table shows these differences.
Criminal law encompasses both substantive criminal law and criminal procedure. Substantive law defines proscribed behaviors and specifies penalties. Laws concerning murder, rape, and robbery are substantive in that they define unlawful acts. Procedural law consists of rules stating how the government proceeds against an individual accused of committing a crime. Trial by jury, the right to counsel, the right to appeal, and the right to face one's accusers are just a few examples of procedural law. Violations of these rights by the government are violations of due process. If the government violates procedural law, that violation can be grounds for appeal and for a reversal of a criminal conviction.
|
|
|